18+ the acceleration vector of a particle in uniform circular motion
A particle can travel in a circle and speed up or slow down showing an acceleration in the direction of the motion. Consequently the acceleration is the second derivative of position often written.

Fragmentation Dynamics Of A Carbon Dioxide Dication Produced By Ion Impact The Journal Of Physical Chemistry Letters
We call the acceleration of an object moving in uniform circular motion the centripetal acceleration a c because centripetal means center seeking.
. In rotational motion the analogous force is torque. Upwards with a uniform acceleration of 5ms-2. Non-relativistic classical mechanics treats time as a universal quantity of measurement which is uniform throughout space and separate from space.
61 Rotation Angle and Angular Velocity. This is also called the moment of force. 66 Satellites and Keplers Laws.
In which r is the position vector of the charged particle t is time and the overdot is a time derivative. An objects mass also determines the strength of its gravitational attraction to other bodies. Amid rising prices and economic uncertaintyas well as deep partisan divisions over social and political issuesCalifornians are processing a great deal of information to help them choose state constitutional officers and.
Circular motion does not have to be at a constant speed. Introduction to Uniform Circular Motion and Gravitation. 181 Electrical Charges Conservation of Charge and Transfer of Charge.
Lastly for motion during which acceleration changes drastically such as a car accelerating to top speed and then braking to a stop motion can be considered in separate parts each of which has its own constant acceleration. Let a particle P be located far from the origin at a point whose position vector is given by. A fictitious force is a force that appears to act on a mass whose motion is described using a non-inertial frame of reference such as a linearly accelerating or rotating reference frame.
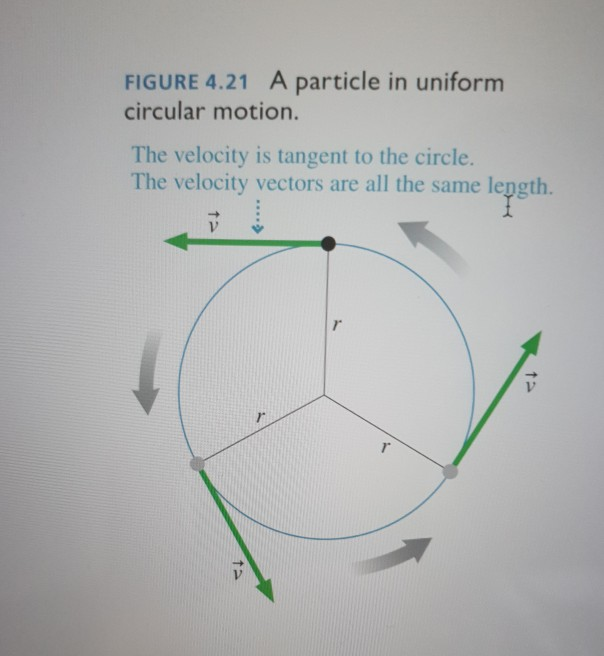
The velocity of the particle changes in magnitude but not in direction. The SI base unit of mass is the kilogram kg. From the first law of motion the direction of velocity vector is tangential to the path of.
If this acceleration is multiplied by the particle mass the leading term is the centripetal force and the negative of the second term related to angular acceleration is sometimes called the Euler force. From Newtons laws we see that since the direction of the velocity is changing there is an. The laws of physics are invariant that is identical in all inertial frames of reference that is frames of reference with no acceleration.
In the case of uniform circular motion a particle moves in a circle with constant speed. Furthermore it assumes that space is Euclidean. Transforming this equation to a reference frame rotating about a fixed axis through the origin with angular.
62 Uniform Circular Motion. Thus the acceleration produced in the particle is zero. June 18 2020.
A particle executing circular motion can be described by its position vector latexmathbfoversetto rtlatex Figure shows a particle executing circular motion in a counterclockwise direction. 64 Fictitious Forces and Non-inertial Frames. MP Board Class 10 Result Declared mpresultsnicin.
In physics mass is not the same as weight even though mass is often. The mathematical tools of vector algebra provide the means to describe. The Graphical Method of Vector Addition and Subtraction.
The value of the constant G was first accurately determined from the results of the Cavendish experiment conducted by the British scientist Henry Cavendish in 1798 although Cavendish did not himself calculate a numerical. Toward the center we say that a particle in uniform circular motion has a centripetal. As the particle moves on the circle its position vector sweeps out the angle latexthetalatex with the x-axis.
Position when thought of as a displacement from an origin point is a vector. Notice that velocity always points in the direction of motion in other words for a curved path it is the tangent vectorLoosely speaking first order derivatives are related to. From the given position-time graph it is observed that it has a constant slope.
Mass is the quantity of matter in a physical bodyIt is also a measure of the bodys inertia the resistance to acceleration change of velocity when a net force is applied. Figure 67 The directions of the velocity of an object at two different points are shown and the change in velocity Δ v Δ v is seen to point approximately toward the center of curvature see small. Classical mechanics assumes that time has a constant rate of passage independent of the observers state of motion or anything external.
See also the article on non-uniform circular motion. We draw the acceleration vector in the direction opposite the velocity vector because the plane is decelerating. 1 Velocity and acceleration are vector quantities as well.
It is related to Newtons second law of motion which treats forces for just one object. In physics the special theory of relativity or special relativity for short is a scientific theory regarding the relationship between space and timeIn Albert Einsteins original treatment the theory is based on two postulates. If the force F is acting on the particle the.
From the instantaneous position r rt instantaneous meaning at an instant value of time t the instantaneous velocity v vt and acceleration a at have the general coordinate-independent definitions. Introduction to Uniform Circular Motion and Gravitation. Because of the direction of the acceleration ie.
Therefore the force acting on the particle is zero. The acceleration of the particle is directed toward the center of the circle and has mag-nitude a v2 r 321 where r is the radius of the circular path and v is the constant speed of the particle. 4 Chapter Review.
A positively charged particle will be accelerated in the same linear orientation as the E field but will curve perpendicularly to both the instantaneous velocity vector v and the B field according to the right-hand rule in detail if the fingers of the right hand are extended to point. This causes angular acceleration in the body which means forcing to change the rotational state of the body. For the remainder of the article it is assumed that the initial velocity v of the particle is not aligned with position vector r ie that the angular momentum vector L r m v is not zero.
For now it is sufficient to introduce the terms and let students know that a vector includes information about direction. Passengers in a vehicle accelerating in the forward direction may perceive they are acted upon by a force. In uniform circular motion the particle executing circular motion has a constant speed and the circle is at a fixed radius.
For example displacement velocity acceleration and force are all vectors. In Newtonian mechanics the equation of motion for an object in an inertial reference frame is where is the vector sum of the physical forces acting on the object is the mass of the object and is the acceleration of the object relative to the inertial reference frame. 61 Rotation Angle and Angular Velocity.
187 Conductors and Electric Fields in Static Equilibrium. 44 Uniform Circular Motion. 188 Applications of Electrostatics.
In a uniform circular motion the particle executing circular motion has a constant speed and the circle is at a fixed radius but the speed of the particle is changing not constant then there will be an additional acceleration that is tangential acceleration which acts. 65 Newtons Universal Law of Gravitation. In one-dimensional or straight-line motion the direction of a vector can be given simply by a plus or minus sign.
Assuming SI units F is measured in newtons N m 1 and m 2 in kilograms kg r in meters m and the constant G is 6674 30 15 10 11 m 3 kg 1 s 2. California voters have now received their mail ballots and the November 8 general election has entered its final stage. These results agree with those above for nonuniform circular motion.
The velocity of the particle changes continuously in direction but not in magnitude. 45 Relative Motion in One and Two Dimensions. Recall that a vector is a quantity that has magnitude and direction.
An Argument for Simplicity. Equations of Motion for Uniform Circular Motion. A quantity with both magnitude and direction.
Every central force can produce uniform circular motion provided that the initial radius r and speed v satisfy the equation.

Velocity Vector And Acceleration Vector In A Uniform Circular Motion Are Related As Youtube

4 4 Uniform Circular Motion University Physics Volume 1

The Acceleration Vector Of A Particle In Uniform Circular Motion Averaged Over The Cycle Is A Null Vector This Statement Is

For A Particle In Uniform Circular Motion The Acceleration Vec A At A Point P R Theta On The Circle Of Radius R Is Here V Is The Speed Of The Particle And
In A Uniform Circular Motion With Constant Speed How Can The Velocity Vary At Different Points Quora

4 4 Uniform Circular Motion University Physics Volume 1

4 4 Uniform Circular Motion University Physics Volume 1

For A Particle In Uniform Circular Motion The Acceleration A At A Point P R Theta On The Circle Of Radius R Is Here Theta Is Measured From The X Axis

Computational Modeling Of Supramolecular Metallo Organic Cages Challenges And Opportunities Acs Catalysis

Problems And Solutions On Mechanics Kepler Sil Academia Edu
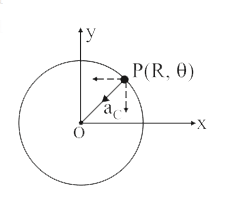
For A Particle In Uniform Circular Motion The Acceleration Vec A At A Point P R Theta On The Circle Of Radiu R Is Here Theta Is Measured From
The Coordinate Of A Moving Particle Are Given By X 4t T 2 2 And Y 3 6t T 3 6 What Is The Velocity And Acceleration Of The Particle When T 2 Quora
The Acceleration Vector Of A Particle In Uniform Circular Motion Averaged Over The Cycle Is A

The Acceleration Vector Of A Particle In Uniform Circular Motion Averaged Over The Cycle Is A Null Vector This Statement Is
The Motion Of A Particle Is Defined By The Relation X 1 3 T3 3t2 8t 2 Where X Is The Distance In Meters And The Time In Seconds What

9 2 Motion Worksheet

Position Vector With Respect To Centre Velocity Vector And Acceleration Vector Of A Particle In Circular Motion Are Vec R 3vec I 4vec J M Vec V